III./9.3. General diagnosis of peripheral nervous system disorders
As for all diseases, the clinical picture (complaints, signs and symptoms) is the most important element in the diagnosis of peripheral nervous system disorders. Table 4 shows auxiliary examinations that provide further help in the diagnostic process.
Table 4: Auxiliary examinations in the diagnosis of peripheral nervous system disorders
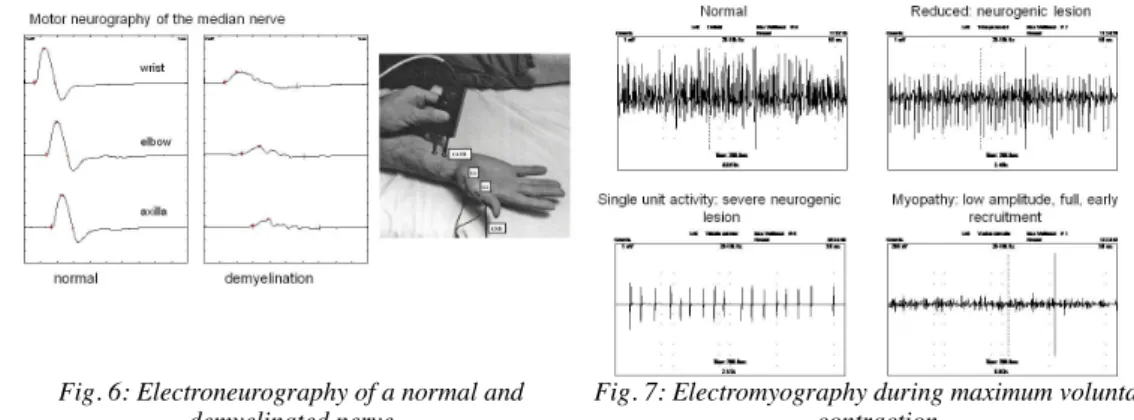
The most important instrumental examination in the diagnosis of peripheral nervous system disorders is the electrophysiological examination: electroneurography / electromyography (ENG/EMG). ENG/EMG (in short EMG) is the only objective method that is able to confirm dysfunction of the peripheral nervous system. In essence, the bioelectric activity produced by nerves and muscles is recorded and assessed during EMG. In electroneurography, motor or sensory nerves are stimulated by electric current and the evoked response (summated action potentials of nerve fibers) is recorded by superficial electrodes. Normal or abnormal function (demyelination or axonal lesion) of the nerve is determined based on the configuration and size of the response, and the calculated nerve conduction velocity (Fig. 6). In electromyography, electric activity generated by muscle fibers during rest and contraction is recorded by a concentric needle electrode inserted into the muscle. Electromyography shows whether the muscle is partially or completely denervated, and it may be used to estimate the number of
functioning motor units and to differentiate between muscle weakness of neurogenic and myogenic origin (Fig. 7). The clinical examination and suspected diagnosis determines exactly which nerves and muscle are sampled during the EMG examination.
Fig. 6: Electroneurography of a normal and demyelinated nerve
Fig. 7: Electromyography during maximum voluntary contraction
The primary role of EMG in the diagnostic process is to confirm the suspected clinical diagnosis, e.g. tunnel syndrome or polyneuropathy. In addition, it provides information about the severity, duration and axonal or demyelinative character of the lesion, and is able to detect subclinical dysfunction as well. All these help the clinician in assessing the prognosis of the disease.