Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework**
Consortium leader
PÁZMÁNY PÉTER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY
Consortium members
SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
The Project has been realised with the support of the European Union and has been co-financed by the European Social Fund ***
**Molekuláris bionika és Infobionika Szakok tananyagának komplex fejlesztése konzorciumi keretben
***A projekt az Európai Unió támogatásával, az Európai Szociális Alap társfinanszírozásával valósul meg.
PÁZMÁNY PÉTER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS
UNIVERSITY
WORLD OF MOLECULES
PROPERTIES OF ATOMS
(Molekulák világa)
(Az atomok tulajdonságai)
KRISTÓF IVÁN
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Previously - Periodic system of elements 1. History of elements
2. Rutherford’s scattering experiment 3. Bohr-Sommerfeld model
4. Elementary particles
5. Fundamental interaction
6. Periodic system/table of elements
[an interactive periodic table is available at www.ptable.com]
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Previously - Rutherford’s atom model (He)
http://http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Helium_atom_QM.svg
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Previously - Elementary particles
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Standard_Model_of_Elementary_Particles.svg
Elementary particles
• Fermions
• Quarks
• Leptons
• Bosons
• Gauge bosons
Fundamental interactions
• strong nuclear force
• weak nuclear force
• electromagnetic force
• gravitational force
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Periodic_table
Previously – Periodic table of elements
1. Nucleus 2. Isotopes
3. Tables of isotopes 4. Radioactivity
5. Decay modes
6. Bohr-Sommerfeld model 7. Quantum numbers
8. Electron structure 9. Examples
Table of Contents
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons Atomic number (Z)
• number of protons
Number of neutrons (N) Mass number (A)
• Sum of protons and neutrons A=Z+N
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Nucleus
Same chemical element
• Atomic number (Z) is the same
Different number of neutrons (N) Mass number (A) different!
e.g.: Carbon
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Isotope
C
C
C 13 6 14 6
12 6
A
Z
• number of protons (Z) vs. neutrons (N)
• all isotopes of the same element are present at constant Z (atomic number)
• different representations
• half-life
• decay mode
• Checker board for following radioactive decay chains
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Table of isotopes – table of nuclides
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Isotopes
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Isotopes_and_half-life.svg
number of protons
number of neutrons
stability
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Isotopes
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Table_isotopes_en.svg
Types of
decay
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
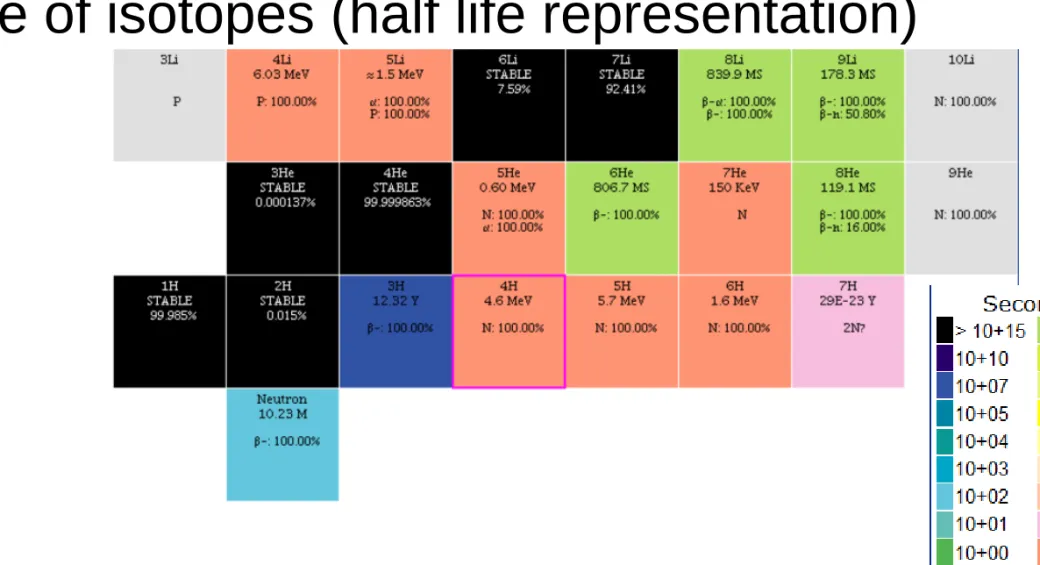
Table of isotopes (half life representation)
National Nuclear Data Center, information extracted from the Chart of Nuclides database, http://www.nndc.bnl.gov/chart/
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Table of isotopes (decay mode representation)
National Nuclear Data Center, information extracted from the Chart of Nuclides database, http://www.nndc.bnl.gov/chart/
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Isotopes of Carbon
Carbon-12 ( 12 C) is used as atomic mass unit:
1 atomic mass unit is 1/12th of 1 mole 12 C.
Or
1 mole is the amount of atoms in 12grams of 12 C.
It is the Avogadro number: 6.022×10 23 mol -1
Different isotopes of the same chemical element have different nuclear stabilities.
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Isotopes of Carbon
Main decay modes of unstable nuclei
• Alpha decay
• The release of 2 protons and 2 neutrons (i.e. a 4 He nucleus), A 2 =A 1 -4; Z 2 =Z 1 -2
• Beta decay
• Release of an electron from the nucleus, Z 2 =Z 1 +1
• Gamma decay
• High energy X-rays
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Radioactivity
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Main decay modes
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Alfa_beta_gamma_radiation.svg
Other decay modes
• Proton emission, neutron emission,
double proton emission, spontaneous fission
• Positron emission (β + ), electron capture,
double beta decay, double electron capture, double positron emission, electron capture + positron emission
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Radioactivity
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Decay modes on the table of nuclides
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Radioactive_decay_modes.svg
• half life: time required for half of the amount to decay
t 1/2
• Decay constant λ
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Radioactive decay chains
λ
) 2 ln(
2
1 =
t N ( t ) = N 0 ⋅ e − λ ⋅ t
Decay chains occur when the resulting nucleus is also unstable.
Decay chains have different decay modes and rates dependent on the properties of the
unstable nuclei.
Decay stops at a stable nucleus
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Radioactive decay chains
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
from 238 U (uranium) to 206 Pb (lead)
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
Decay chain of Uranium-238
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Decay_chain%284n%2B2,_Uranium_series%29.PNG
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Table of isotopes (decay mode representation)
National Nuclear Data Center, information extracted from the Chart of Nuclides database, http://www.nndc.bnl.gov/chart/
Z
N
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_nuclides
semmelweis-egyetem.hu
World of Molecules: Properties of atoms
Electron configuration of atoms
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Electron_Configuration_Table.jpg