ГЧ A Т^Т
... -m
K F K I - 1 9 8 0 - 9 3
В , V A S V Á R I
E L E C T R O N D E N S I T I E S O F L I Q U I D A N D A M O R P H O U S M E T A L S
' Hungar i an ‘Academy o f ‘S ciences C E N T R A L
R E S E A R C H
I N S T I T U T E F O R P H Y S I C S
B U D A P E S T
KFKI-1980-9 3
ELECTRON DENSITIES OF LIQUID AND AMORPHOUS METALS
B. Vasvári
Central Research Institute for Physics H-1525 Budapest 114, P.O.B, 49, Hungary
To appear in the Proceedings of the Conference on Metallic Glasses:
Science and Technology, Budapest, Hungary, June 30 - July 4, 1980;
Paper E-18
HU ISSN 0368 5330 ISBN 963 371 739 6
АННОТАЦИЯ
С использованием математических методов, применяемых для расчета струк
туры полос кристаллических материалов, разработан метод определения локаль
ных плотностей электронных состояний в структурно-неупорядоченных металлах.
Целью разработки являлась разработка простого, но реально описывающего алго
ритма для определения плотностей состояний. Вследствие изотропности этих си
стем имеется возможность существенного упрощения, если при расчетах до конца придерживаться представлению данных в форме координат. Приведены предваритель
ные цифровые результаты для аморфного железа.
KI VONAT
Egy eljárást fejlesztettünk ki a szerkezetileg rendezetlen fémek lokális elektron-állapotsürüségeinek (DOS) meghatározására a kristályos anyagok sáv- szerkezetének számítására szokásos matematikai módszerek felhasználásával.
A célkitűzés egy egyszerű, mégis realisztikus algoritmus kifejlesztése az ál- lapotsürüség meghatározására. A szóbanforgó rendszerek izotrópiájának kö
vetkeztében lényeges egyszerüsitési lehetőségek adódnak, ha a számítások so
rán mindvégig a koordináta-reprezentációban maradunk. Előzetes numerikus eredményeket mutatunk be az amorf vasra vonatkozóan.
ABSTRACT
A f o r m a l i s m is d e v e l o p e d to c a l c u l a t e the local d e n s i t y of states (DOS) in a structurally d i s o r d e r e d metal u s i n g the m a t h e m a t i c a l techniques of band structure c a l c u l a t i o n s of c r y s t a l l i n e materials.
The aim is to develop a simple, b u t r e a l i s t i c a l g o r i t h m for the c a l c u l a t i o n of the DOS. R e m a i n i n g c o n s i s t e n t l y in the direct space t h r o u g h o u t the w h ole calculation, a consid e r a b l e s i m p l i f i c a t i o n occurs due to the isotropy of the systems involved. P r e l i m i n a r y results for amorphous iron are presented.
INTROD U C T I O N
R e a l i s t i c calcul a t i o n s for the e l e c t r o n i c d e n s i t y of states (DOS) of s t r u c t u r a l l y d i s o r d e r e d metals usu a l l y a p p l y the G reen's function f o r m a l i s m and the m u f f i n - t i n a p p r o x i m a t i o n [1]. S i m i larly to the case of c r y stalline metals, e x p a n s i o n s in the m o m e n t u m (k) space and ang u l a r m o m e n t u m (L = (£,m ) ) r e p r e s e n t a t i o n s lead to the K o r r i n g a - K o h n - R o s t o c k e r (KKR) type of formulas and an i n d irect r e l a t i o n s h i p b e t w e e n the q u a s i - p a r t i c l e energy, E, a n d the wave n u m b e r vector, k,in the r e c i p r o c a l space. Due to the lack of
t r a n s l a t i o n a l invariance in a m o r p h o u s m etals, the w a v e number vector, k, is not a go o d q u a n t u m n umber for the one elec t r o n
states, therefore, c o m p l i c a t i o n s occur, like c o m p l e x wave n u m b e r vectors, finite lifetimes in the state k, etc. In t h i s -paper, we do also use the G reen's f u n c t i o n f o r m a l i s m and the m u f f i n - t i n approximation, but w i t h o u t i n t r o d u c i n g any w a v e - n u m b e r d e p e ndence into our formalism, in other w ords, we use c o n s i s t e n t l y the d i rect, c o o r d i n a t e r e p r e s e n t a t i o n s of our quantities. As a c o n s e quence we g e t rather simple r e s u l t s for the d e n s i t y of states in s t r u c t u r a l l y d i s o r d e r e d systems like liquid m etals or m e t a l l i c g l a s s e s .
2
A S U R V E Y OF THE M A T H E M A T I C A L T R E A T M E N T
In the following o n l y a short outline of the m a t h e m a t i c a l t r e a t m e n t can be given. The starting point is an e x p r e s s i o n for the local DOS, g(r,E), in the t e rms of i m m a g i n a r y p a r t of the e n s e m b l e a v e r a g e d G r e e n ' s function of the t o t a l system:
g(r,E) = - ^ lm < G(r,r,E)>. (1)
It is supposed that the p o t e n t i a l of the a m o r p h o u s s y s t e m can be w r i t t e n as s u p e r p o s i t i o n of n o n - o v e r l a p p i n g a t o m i c - l i k e p o t e n tials :
V (r) = E v, (r-R ) .
— lR.
Here v^ir-F^) is the m u f f i n - t i n p o t e n t i a l a r o u n d the i-th a t o m c e n t e r e d at the p o s i t i o n R^.
It is w e l l known, the Green's function can be e x p a n d e d in the terms of the t-matrices, t., of the i n d i v i d u a l scatterers
l
G = G + E G t.G + E G t.* E G t.*G о i о г о . о r j + . о D о
+ E G t • E G t.* E G tn'G + ...
О i . . . о . О * О
i j+i J
(2)
w h e r e Gq is the f r e e - e l e c t r o n propagator. U s i n g a s imple change of the variables, the R^ d e p e n d e n c e can be t r a n s f o r m e d from t. = t (r-R. ,r.'-R. ) to the G 's: G >-G.. = G (r-r'- R .+ R .) . N e x t we suppose th a t we h a v e a simple, one c o m p o n e n t system, and assume, that the s c a t t e r i n g p r o p e r t i e s of the i n d i vidual atoms are all the same, i.e., the t^ m a t r i c e s are i n d e p e n d e n t of w h i c h a t o m is considered. T h i s a s s u m p t i o n is e q u i v a l e n t to the a verage t - m a t r i x a p p r o x i m a t i o n (ATA), w h e n the s c a t t e r i n g m a t r i x of the i n d i vidual atoms in a r a n d o m s y s t e m is r e p l a c e d by an average t-matrix.
A f ter a s t r a i g h t f o r w a r d a l g e b r a one g e t s for the density of e l e c t r o n s of E energy, inside a m u f f i n - t i n sphére
3
g(r,E) = -j=- и S R„ (r)Rj (r) Y_ (r)Y_ (r) 4Tl LxL 2 ll %2 L 1 L 2
6T -lm - E j “ 1. M TT L 1L 2 И L L 1L L L 2
(3)
Here R^(r)YL (r) is the r egular s o l u t i o n of the radial Schrödinger e q u a t i o n with the m u f f i n - t i n p o t e n t i a l and for the
2
energy E = и . The matr i c e s J and M are de f i n e d as follows:
J = [1-tD] ,
L1L2 L1L2
(4)
[tD]
L 1L 2
— tn • E В _ (R,x) , 2 R+o L 1 2
(5)
M L 1L 2
E t^, 2 By -rt (— R,x)B^ (RfX) t
L' R*o 1 2
(6)
where t^ = t^(x) a n d L are the e x p a n s i o n cofficients of the t-ma t r i x and the fre e - p a r t i c l e Green's functions, respectively, defined in the t e rms of phase shifts, л £ (E), and of the s p h e r i c a l Hankel functions, (xR) in the following way:
1 irU (E)
tÄ = - sin h£ (E)e , (7)
(£ - a')
B_ T (R,h ) = - 4nix E i 1 2 C T _ _ ,YT , ( R ) hl,(xR). (8)
L 1L 2 ~ L' L 1L 2L L
Equa t i o n (3) gives the density of e l e c t r o n s only for a g i v e n
configuration of t h e atoms, r e p r e s e n t e d b y their coordinates, R ^ . To calculate the e n s e m b l e a verage of g(r,E) one has to m a k e some a s s u mption for the d i s t r i b u t i o n of atoms in the system, the n to define a decoupling scheme, h o w to c a l c u l a t e the m a n y - p a r t i c l e averages in e q u a t i o n (3). A p a r t i c u l a r l y simple formula is r e sulted if one s u p p o s e s that the atomic d i s t r i b u t i o n s can be r e p rese n t e d by a s p h e r i c a l l y symmetric p a i r d i s t r i b u t i o n function, g(R) and if, for the higher o r d e r terms, one applies Ki r k w o o d ' s d e c o u p l i n g schemes. In that case the s u m in the (tD) and (M) matrices, over the atomic coordinates, c a n be repl a c e d by i n tegrals containig the function g ( R ) . Due to the isotropy of this d i s t r i b u t i o n the a b o v e m e n t i o n e d m a t r i c e s are diag o n a l ones, and the inverse of J c a n easily be calculated. C a r r y i n g out the in-
4
tegrations w i t h respect to the a n g u l a r coordinates one gets the very simple final formulas for this case as follows:
, _. к „ 2H+1 n 2 . . 0 ( r ' E) * i
I
T Í T V r ), _ 1 - 1
1 - I m —
к
Ü M, (9)J « ■ Ч - « ” *' - - 4npo t )tI (10)
M, = - ( 4 п н ) 2 E H,„
** Z r Z " ^ ^
( I D
where p is the average density of the material, the simple n u m bers D (£,£{£") can e a s i l y be c a l c u l a t e d from the C l e b s c h - G o r d o n coefficients, and the I and are integrals:
I = e R g(R)RdR, о
(12)
H £ = I h * 2 (nR)g(R)R2dR. (13)
о
The integral of p(r,E) inside the atomic v olume with respect to the c o o rdinates r leads to the local density of states, p(E).
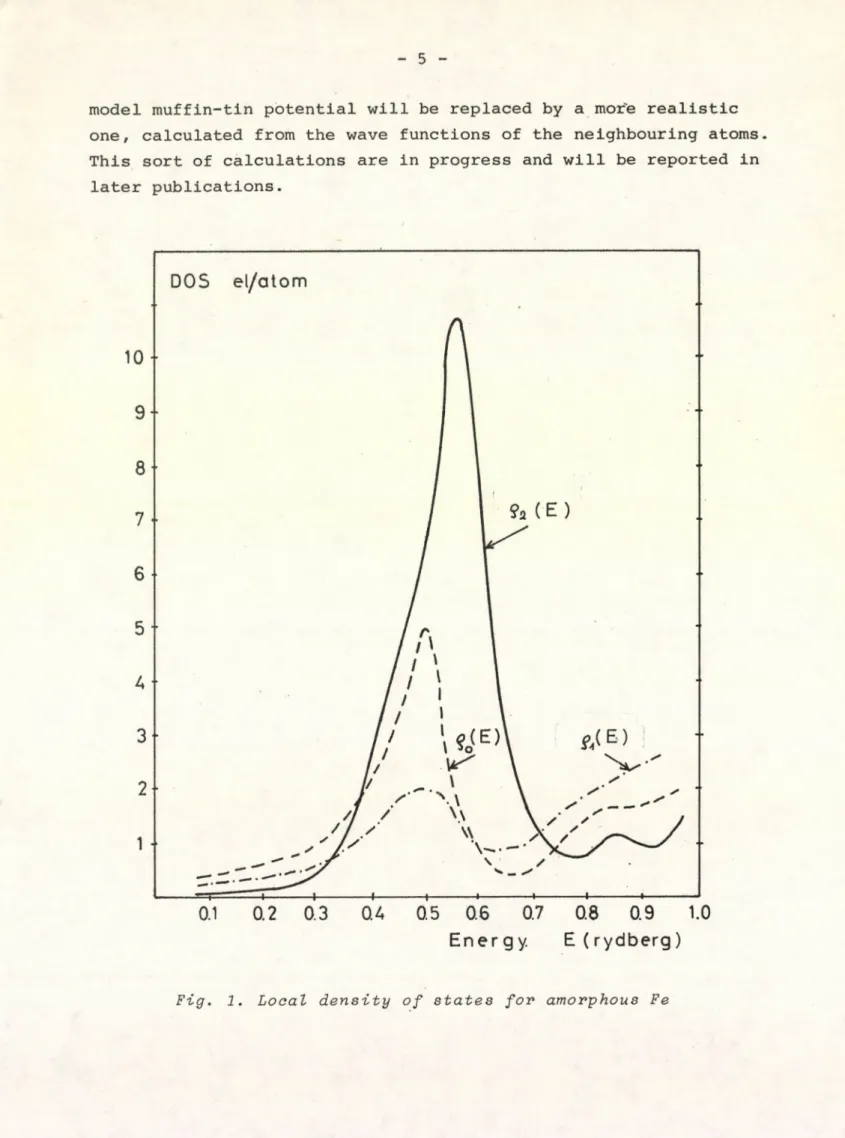
P r e l i m i n a r y numerical calcul a t i o n s wer e p e r f o r m e d for liquid or amorphous iron. The g(R) pair d i s t r i b u t i o n function was c a l c u lated from the analitical structure factor of the h a r d sphere solution of the Per c u s - Y e v i c k equations. The m u f f i n - t i n potential was given by a simple analytical expression, the onl y p a r a meter of it was ch o o s e n to reproduce the resonance in the p hase- shift. U sing these ingredients a s i n g l e - p e a k e d local density of states curve was resulted (Fig. 1.), which, in our model, cor
responds to a single scattering c e n t e r e m b e d d e d into a medium.
The effect of this m e d i u m is e x p r e s s e d by the diag o n a l matrices and , and resulted in the b r o a d e n i n g of the r e s o n a n c e level c h a r a c t e r i s t i c for transitional metals.
To improve the m o d e l d e s c r i b e d we intend to take into a ccount the local e n v i r o n m e n t of the i n d i vidual atoms by d i v i d i n g the sums over R^ in formulas (5) and (6) into two parts. In the first one the R^ takes the values of the few neighbours a r o u n d the original atom, creating a cluster, in the second p a r t s R^ runs over the a t o m i c coordinates outside of this cluster. Also, the
5
m o d e l m u f f in-tin p o t e n t i a l w i l l be r e p l a c e d by a mor e realistic one, calculated from the w a v e functions of the n e i g h b o u r i n g atoms.
This sort of c a l culations are in progr e s s and w i l l be reported in later publications.
Fig. 1. Local density of states for amorphous Fe
6
R E F E RENCE
[1] L. Schwartz, H. Ehrenreich: Annals of P h y s i c s 6£, 100-148 (1971);
L. Schwartz, H.K. Peterson, A. Bansil: Phys. Rev. B 1 2 , 3113- 3123 (1975);
J. Bethell, J.L. Beeby: J. Phys. F: Metal Phys. 1_, 1193-1205 (1977);
S. Asano, F. Yonezawa: J. Phys. F: Metal Phys. 10, 75-79 (1980).
61 -OQ 3
Kiadja a Központi Fizikai Kutató Intézet Felelős kiadó: Tompa Kálmán
Szakmai lektor: Hargitai Csaba Nyelvi lektor: Hargitai Csaba Gépelte: Végvári Istvánná
Példányszám: 220 Törzsszám: 80-633 Készült a KFKI sokszorosító üzemében Felelős vezető: Nagy Károly
Budapest, 1980. október hó